ajDeleteRec function
Description
The ajDeleteRec function is used for deleting records from a database table. Please take note that to run this function from Excel, you would need to set up the DB Connection String from the Properties dialog box.
Syntax
ajDeleteRec(table_name, [column_headers], [data], [filter_type], [filter_condition], [table_schema], [data_source_id], [run_condition], [run_by_function_point_only])
| Argument Name | Description |
|---|---|
| table_name (required) | Specify the name of the table where the records should be deleted from. |
| column_headers (Optional) | Specify the columns to be matched. It can be a range of single row or column that each cell for a column. The cell value can be the actual column name or a data name which is defined in DB Schema. All key columns need to be specified. CLOB and BLOB columns are not supported. |
| data (Optional) | Specify the range for the key field value(s) of the record to be deleted. The orientation can either be landscape or portrait. The orientation should be the same as column_headers. |
| filter_type (optional) | Specify the type of filtering. 3 types are supported 0, 1 and 2. You would need to either provide filter_type+filter_condition or the DB Schema to call this function. Otherwise, an error will be raised. |
| filter_condition (optional) | Specify the range that defines the filter condition. When filter_type = 0. The range defines the where clause of a SQL statement. The range will be concatenated into a single string. For example Name = 'peter' and class = 'B'. filter_type = 1. The range defines the filter condition in the Kendo grid style. There are 6 columns in the range. The first row defines the header. They are Data Name, Operator 1, Search Criteria 1, And / Or, Operator 2, Search Criteria 2. The following operators are supported:
filter_type =2. The range defines a filter condition similar to the format used in MS Query. Two columns are used to define one filter condition. So the number of columns should always be a multiple of 2. E.g. 2, 4, 6. The first column defines the operator and the second consider defines the value. For example, < 10 * Notes An error will occur if the range value is not in the format of the corresponding filter type. For filter_type = 1 or 2, if the operator is available but operand is empty, it will be treated as '' (i.e. empty string). If filter_type = 2, it will validate the correctness of Column Header and DataType against database schema. |
| table_schema (optional) | Specify the range that defines the DB Schema. You need to either provide the filter_type+filter_condition or the DB Schema to call this function. When the DB Schema is provided, the key column(s) must be included in the Column_headers and Data. Otherwise, an error will be raised. |
| data_source_id (optional) | Specify the data source ID. The parameter is used to define which database should be executed for the function. If you do not specify anything, the default value will always be 'primary'. |
| run_condition (optional) | The function will run when the value is TRUE. Otherwise, it will not run. If you do not specify anything, the default value will always be TRUE. |
| run_by_function_point_only (optional) | If it equals FALSE, the function can be executed through ‘Excel Calculation’ (can be either Automatic or Manual, Calculate Now or Calculate Sheet) or Run Function Point. If it equals TRUE, the function can be executed with Run Function Point (AlchemyJ toolbar \ Run Function Point) only. If you do not specify anything, the default value will always be TRUE. |
The function will return:
1) Content type: Number of affected records.
2) Method: Within a cell / cell array
Example
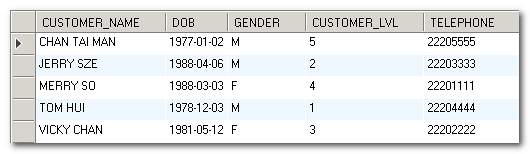
We will use the following table in our examples. The table name is tb_customer. It has 5 columns and 5 rows.
Example 1
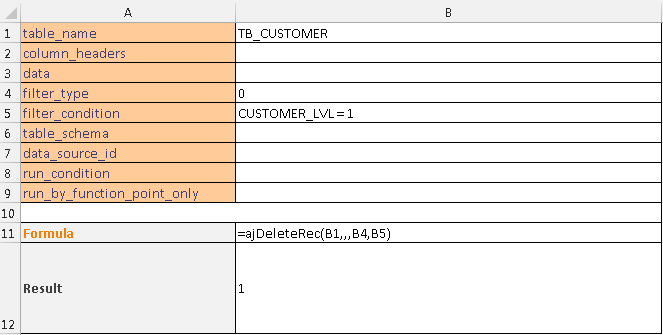
This example deletes records from a tb_customer which Customer Level is 1.
Example 2
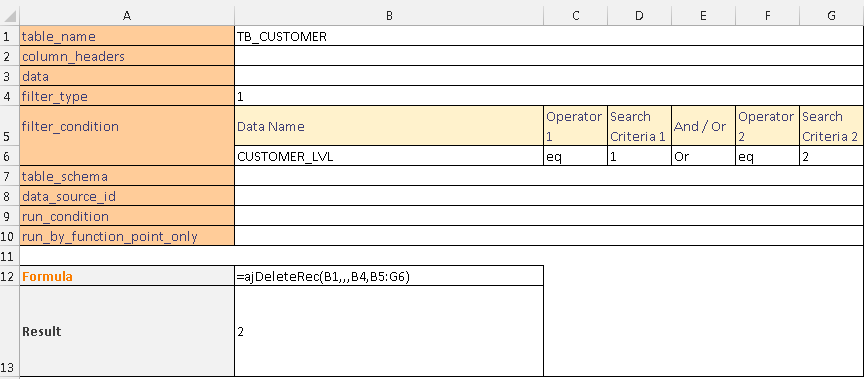
This example deletes records where customer level equals 1 or 2 using filter_type 1.
Example 3
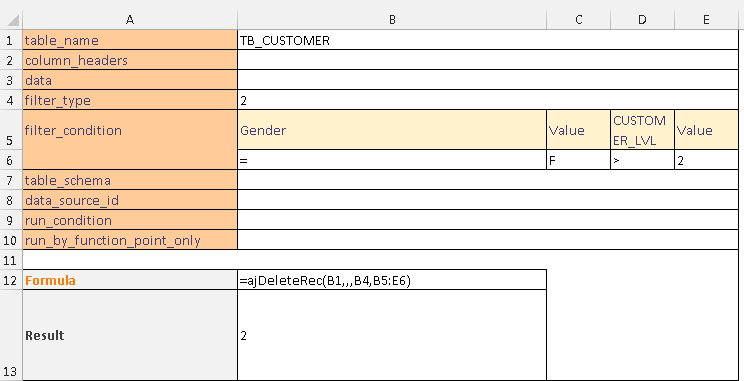
This example deletes records where gender equals "F" and customer level greater than 2 using filter_type 2.
Example 4
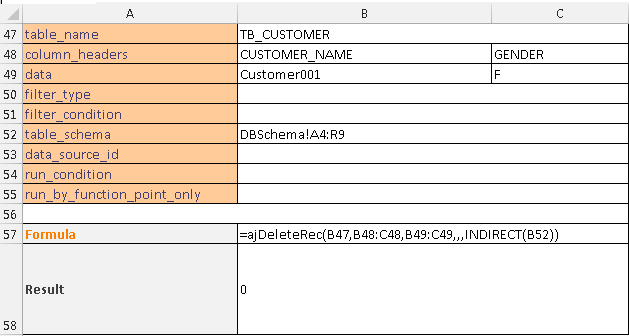
This example deletes records using the DB Schema. column_headers and data need to be specified when using the DB Schema and the key columns must be specified in the column_headers.